Who was Edgar Degas?
Edgar Degas was a famous French artist born in 1834 and played a fundamental role in shaping modern art. It was Impressionism that he was connected to, but he had his way of composition, which made him different from his fellow painters. Prized by his sharp feeling for the movement of people, Degas repeatedly shows ballet dancers, horse races, and everyday scenes with the rare skill of recording the movement and emotion. His extreme care and revolutionary use of uncommon storylines thwarted the artistic standards of the past.
Degas’s obsession with light and colour prompted him to explore different approaches, such as cutting off figures and choosing unexpected ways of positioning figures. He tended to freeze those brief occasions, alighting them with a feeling of spontaneousness and life. Degas not only had an artistic impact but also functioned as a central figure in the impressionist movement and left his mark on the art world. He had traits similar to Impressionist artists, but his foregrounding of line and form made him stand out from the crowd. The life works of Edgar Degas persist to remind us of his revolutionary thinking and his continuing effect on the development of contemporary art.
Beginnings and Artistic Formation
Overview of Degas’s early life, education, and key Influences
Edgar Degas came from a well-off Parisian family, steering him toward a legal career. Nevertheless, his passion for art stood him on a very different path. Degas got a formal education from the École des Beaux-Arts, under Louis Lamothe’s tutelage, where he mastered classical technique. His artistic inclinations were shaped profoundly by the creations of Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres and Eugène Delacroix so that their styles continued to be reflected in his creative works.
While in Italy, Degas was surrounded by Renaissance art, and it was here that he learned the techniques and the principles of the Renaissance. Such training, in addition to his encounter with Japanese woodblock printing, photography and the Impressionist movement, turned out to be a crucial factor in shaping his style. These multifaceted sources of inspiration eventually amounted to his unique style, which was defined by his creative composition, meticulousness, and proficiency in depicting movement and emotionality in his part.
From classicism to Innovation
Degas’s initial classical training and his shift towards more innovative, experimental techniques that characterized his mature work
Edgar Degas commenced his artistic journey with a groundwork in classical training at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, learning old-style methods and principles. Degas was greatly affected by the art of Ingres and Delacroix in his early works, and he insisted on the classical standards of beauty and form. While he was firmly attached to traditional formative influences, later on, as an artist, he succeeded in trying new ways of expressing his vision.
Degas’s focus with conventionality and insistence on experimentation and discoveries can be seen in his late artworks. He would transcend the traditional themes in his artworks, as he depicted scenes of modern urban life, including dancers, laundresses, and horse races. By controlling the composition of the work using uncommon angles and focusing on the interaction of light, colour, and motion, Degas created paintings that went beyond the artistic standards of his time. He started this way by taking an interest in catching the instantaneous and the ordinary activities with a bit of spontaneity, creating his distinct way of working. Using brisk cropping, striking angles and human figures in action, Degas helped shape the art world and created new pathways for future artists to open their minds to many options.
Degas and Impressionism
Examine Degas’s complex relationship with the Impressionists
Edgar Degas had a complex bond with the Impressionists, contributing significantly to their exhibitions. He shared with the Impressionists the common ground of depicting daily life in a way that was not staged and represented the effects of light, but he diverged by focusing on finely drawn details rather than quick brushstrokes. His works frequently applied the interior set as the background and concentrated on the details of current life. While a member of the Impressionist movement, Degas did not develop his style; instead, he stayed faithful to the form and structure and did not follow Impressionist techniques. He was famous for his attention to technical details and the desire to find unusual angles. This made him different from other art painters. Later on, he adopted a middle-of-the-road ground, which, as a result, allowed him to maintain his individuality and incorporate the characteristics of Impressionism into his works.
Pioneering Techniques and Subjects
Edgar Degas revolutionized the art world and helped create new techniques and subjects. He was very creative and used perspective and composition in a non-traditional way, as seen in his approach of placing the subject off-center and using unusual angles to make his art different. Degas’s obsession with motifs such as dancers, racehorses, and laundresses were about how he was interested in including their movement and daily activities in his paintings in a new way. Dancer’s art was one of Degas’ favourite subjects, and it exhibited his cautious research of movements and forms and made him stand out from his peers. Moreover, the artist’s utilization of pastels in his painting gave him a new, lively colour range that brought to life the lines and depth he wanted to express.
Masterpieces of Movement and Light
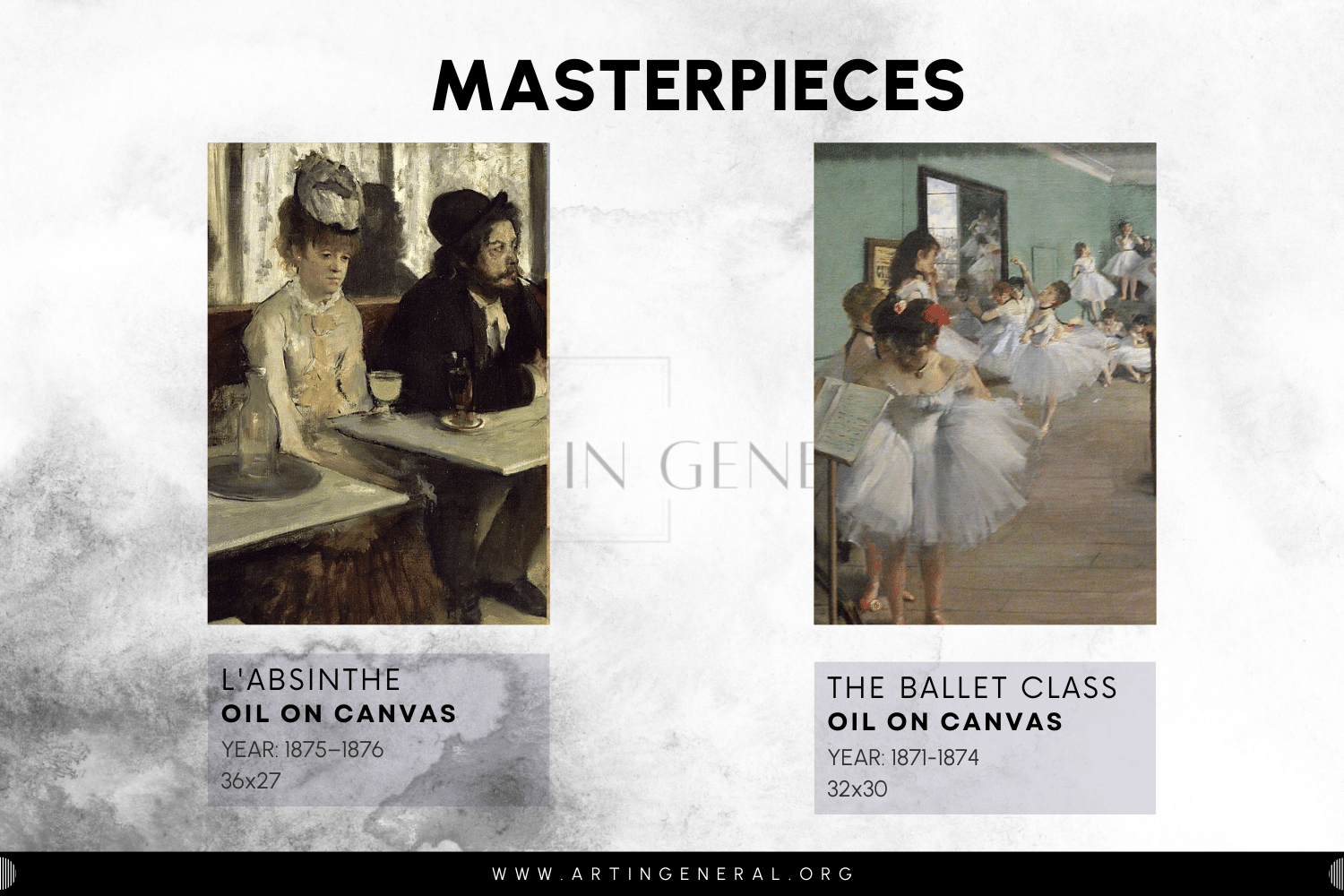
Edgar Degas’s ‘The Ballet Class’ and ‘L’Absinthe’ are two outstanding examples of movement, light, and psychological depth.
The Ballet Class, Year: 1871-1874. Oil Canvas. Musée d’Orsay in Paris, France.
‘L’Absinthe’ underscores the interaction of light and shadow to create an impression of motion and enthusiasm to display the skill and elegance of the dancers. The ability of Degas to comprehend forms of human anatomy and movement is depicted through his attention to details and portrayal of dancer’s stances and faces.
However, ‘L’Absinthe’ goes further by emphasizing the psychological aspects of the situation, which are revealed in the intricate and deep complexity of the emotional state of the characters. By adding the light and shade elements, this painting captures the gloomy atmosphere and the disturbed consciousness of the characters portrayed. The unique technique that Degas uses to combine his artwork’s movement, light, and psychological in-depth shows his genius ability to capture short moments in time and make the viewers feel profoundly emotional.
The artist’s Eye: Degas’s Portraits
Degas’s approach to portraiture, including his candid depictions of Parisian lie and notable figures.
When Degas depicts his subject matter, he represents a one-of-the-kind perspective that shows the core of Parisian life and the life of the French people. Through his portrayals, he explores many human emotional and social nuances in his own time. The truthfulness and skill of Degas, when it comes to giving detail to his figures and how he delivers the expression of their feelings through gestures, create the unique ability to disclose the inner self of his subjects, with his superior skills at revealing the essence of his subjects, whether ordinary Parisians or world-renowned personalities, he outshines others by exploring the depth of their inner beauty. Degas creates an atmosphere of closeness and sincerity through his paintings rather than just pictorial representations. This transformation makes the subjects more than faces; instead, they become complex characters with different stories behind each of them
Degas’s legacy in Art
L’Absinthe
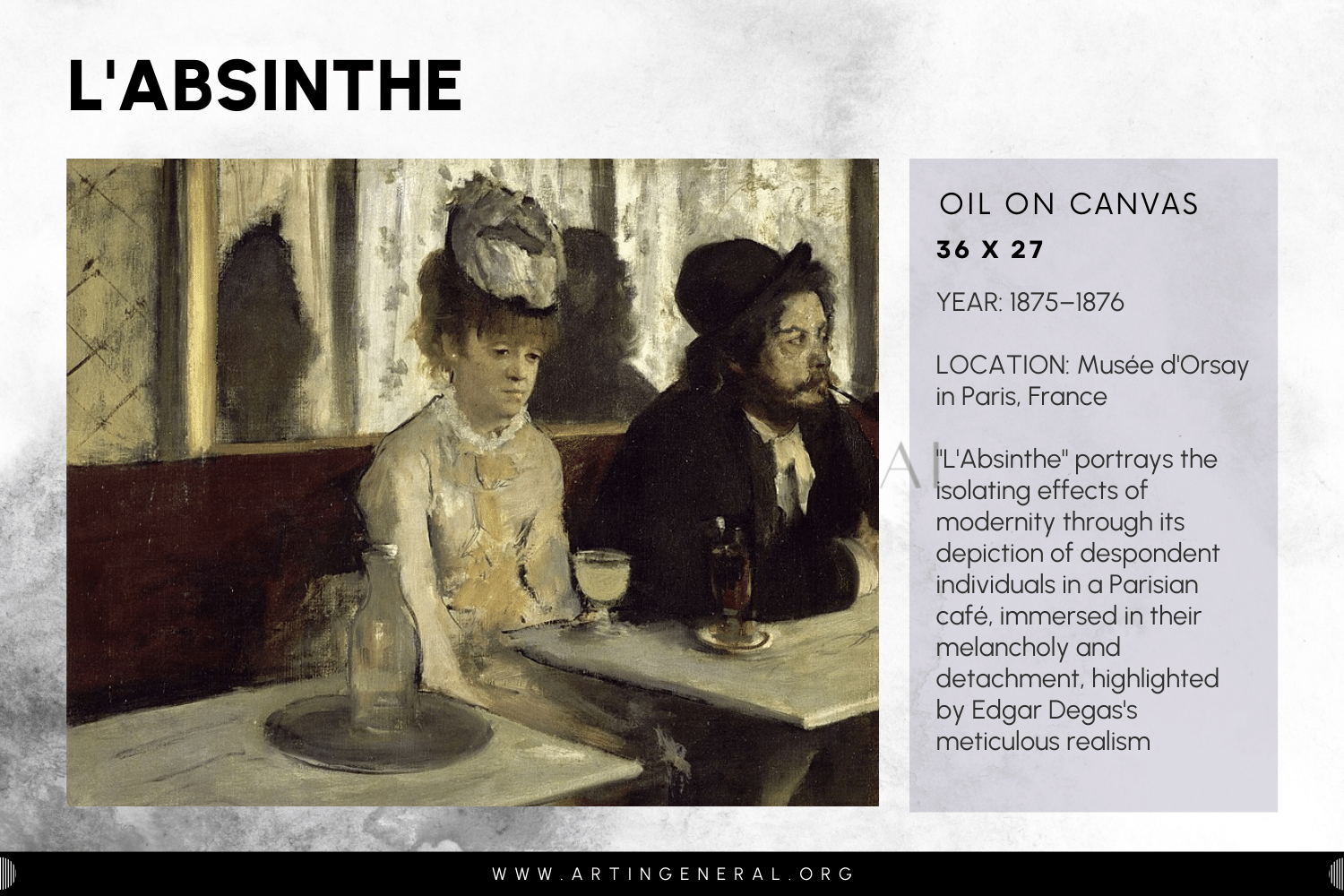
- Name: L’Absinthe
- Artist: Edgar Degas
- Year: 1875–1876
- Medium: Oil Canvas
- Location: Musée d’Orsay in Paris, France
Degas’s legacy in art reflects through generations, shaping various artistic movements and mediums. The composition of his milestone work, “L’Absinthe” (1870), is a testament to his talent for capturing raw human feelings and social issues. The painting is at the corner of a bar in Paris, where the artist Degas demonstrated his ability to express the complex human experience.
Degas’s groundbreaking compositions, lighting and shadow, and emphasis on everyday life have impacted enormously many artists, such as Impressionists and Modernists. He provided the head start for creating this aesthetic in snapshots in photography and early cinema based on realism by concentrating on moments that pass by quickly and on straight expressions.
Young Spartans Exercising

- Artist: Edgar Degas
- Year: 1860
- Medium: Oil Canvas
- Location: Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute in Williamstown
‘Young Spartans Exercising’ subjects are Spartan men, a young warrior doing movements, and this is evidence that Degas here is indicating his interest in movements and human form. Artwork enhances the classical notion of physical power and order orchestrated by the young man, creating a sense of freshness, youth, and athletic skills that are the main characters in the composition. Degas’ everlasting attention to detail and his skill to portray movement in his different strokes produce a very dynamic and lively composition that enchants the viewers and makes them see the beauty and power of the human body in all its forms.
The Bellelli Family
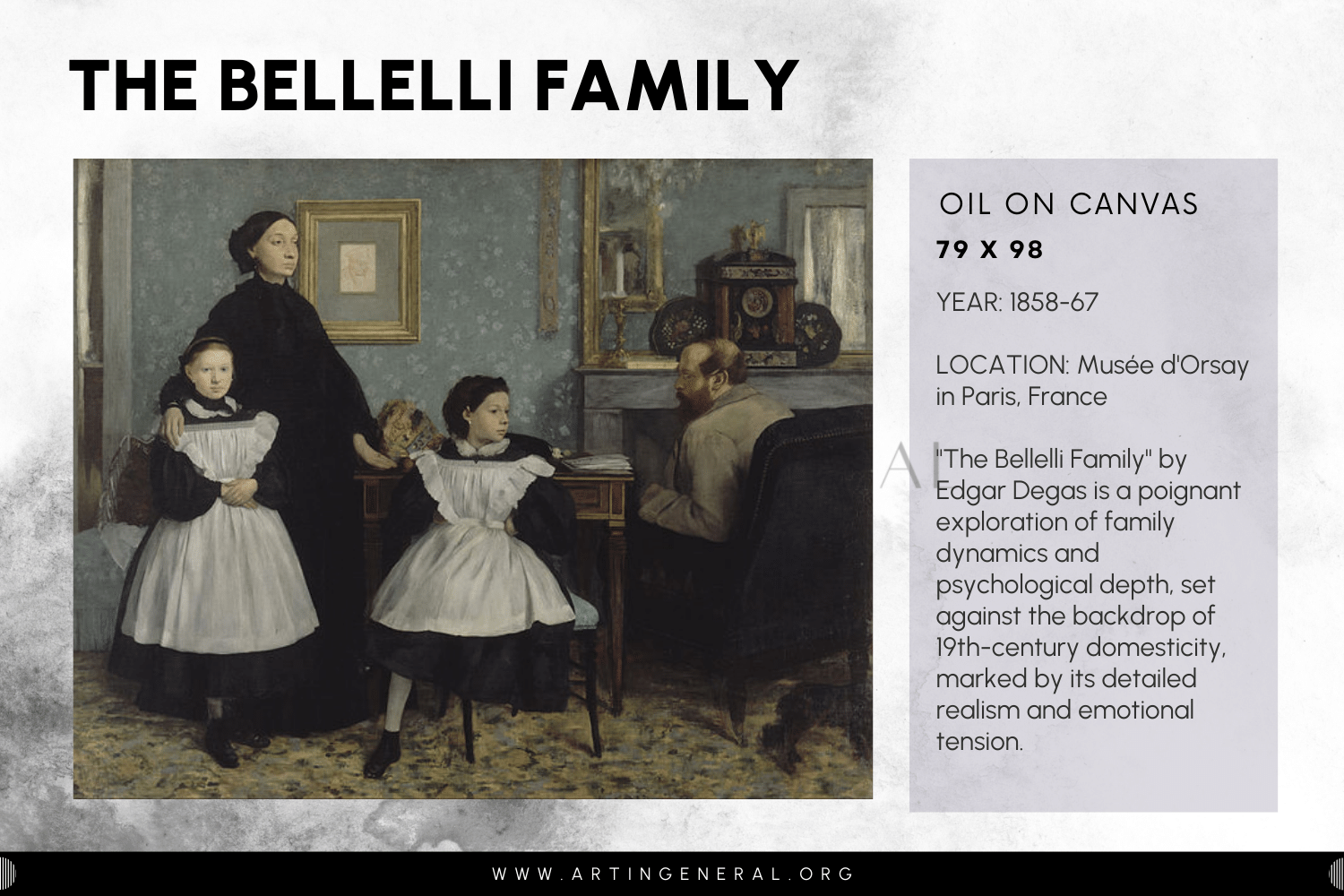
- Name: Artist: Edgar Degas
- Year: 1858-67
- Medium: Oil Canvas
- Location: Musée d’Orsay in Paris, France
Edgar Degas’ portrayal of the Bellelli family depicts his artistic skills and use of light, colour and realism. The entire composition of this painting is cast in a gentle, natural light that softly shines on the figures, and as a result, it looks like they are enjoying the warmth and depth of a very cozy space. The cleverly used colour scheme of low-key colours reinforces the piece’s mood and accentuates the inner workings of the family’s emotional turmoil. Degas is notable for his accuracy and ability to portray the subtleties of human expression and relationships, which collectively contribute to this masterpiece’s genuine feel and layered psychological depth.
Orchestra Musicians
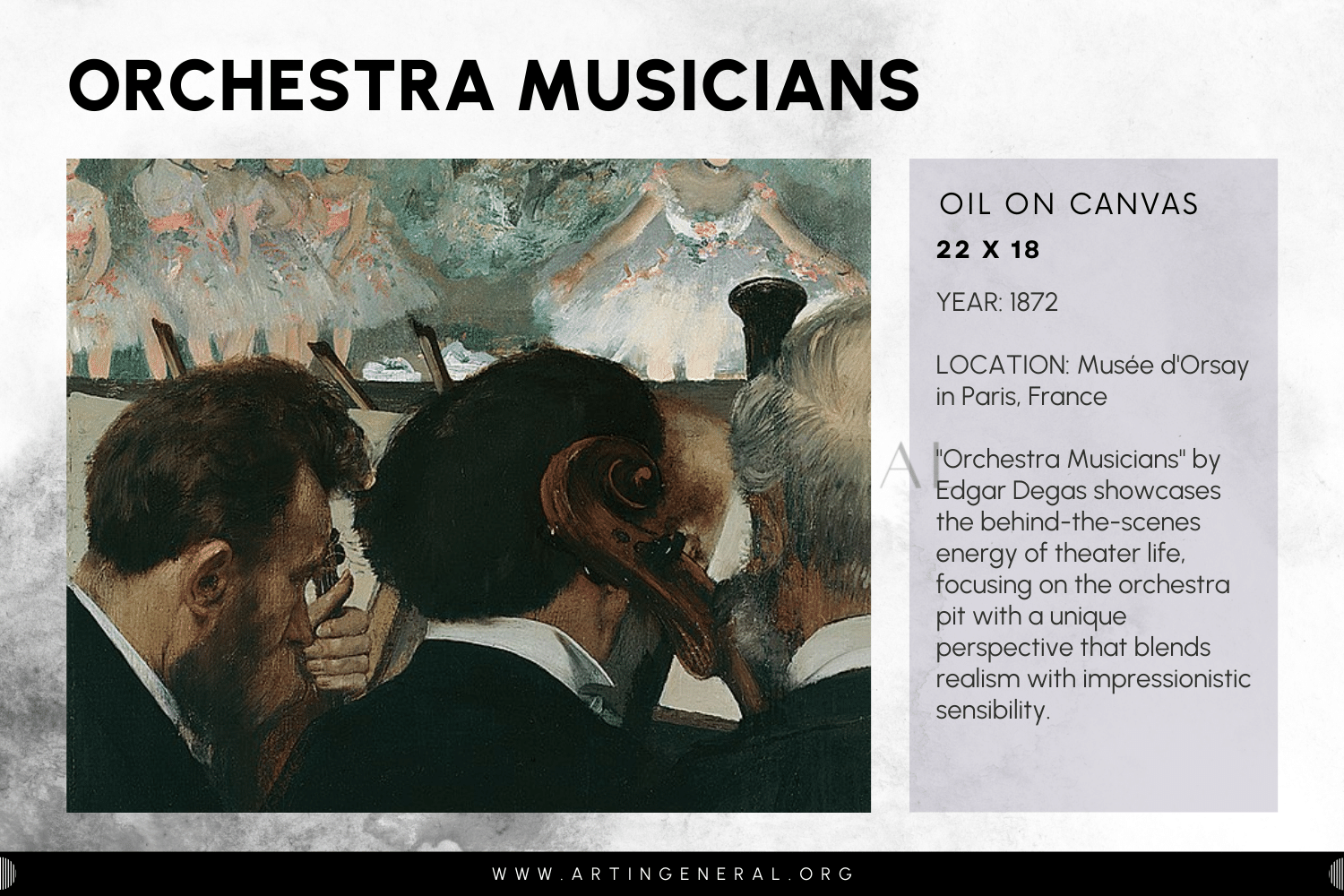
- Artist: Edgar Degas
- Year: 1872
- Medium: Oil Canvas
- Location: Musée d’Orsay in Paris, France
Edgar Degas dexterously integrates light, color, and realism to portray a scene of musicians in action. Through the use of light and shadows on the figures, the movie presents the feeling of movement and depth, but such a dynamic effect can improve the atmosphere of this performance. Degas’ lightness in coloring makes the composition more vibrant. At the same time, his utmost attention to detail captures the focus on each musician and their passion, stirring the final piece with a sense of realism.
Challenges and Critiques
Edgar Degas, famous for their impressionist works, encountered difficulties with people because his opinion on society and art was rather harsh. He was criticized for his unkind portrayals of certain aspects of modern people’s lives, mainly how they depicted the dancers, which some perceived as unreasonable. Unlike his predecessors, Degas was praised for his unique approach to composition and found himself accused of having a pessimistic attitude towards life.
The Sculptural Work of Degas
Degas’s sculptures, particularly ‘Little Dancer Aged Fourteen,’ were an authentic yet unusual topic and denoted a significant break from traditional old-style sculpture. The artwork was praised and criticized initially, but it won recognition as a masterpiece with its more complex artistic expressions and high level of detail. Degas’ sculptures were unconventional because they needed to fit the common understanding of the shape and theme. Degas has been an inspiration to many of the artists who followed him.
Preserving Degas’s Heritage
Digital archives, museum exhibitions, and large-scale conservation activities are all aimed at keeping Degas’s works in good shape. To guarantee that the full range of Degas’s artistic work can be enjoyed by future generations, exhibitions have played an important role of rounding up his work starting from the more known to the lesser know works and pastels.
Degas Influence on Modern and Contemporary Art
Edgar Degas’s impact on current and contemporary art is crucial. He practised composition, light, and regular subjects with his works; they greatly motivated the artists. His concepts of motion, seclusion, and self-reflection are still imitated in contemporary art today, resulting in the timelessness of his art world.




Leave a Reply